GMAT R2022a Released

The GMAT development team is pleased to announce the release of GMAT version R2022a. New features in this release include TLE and covariance propagation, N-plate SRP models and solve-fors, an operational Extended Kalman Filter Smoother, planetographic (e.g., South Atlantic Anomaly) region entry and exit calculations, an Initial Orbit Determination (IOD) capability and contact calculations using station masks. In addition, the API interface is now production quality. For a complete list of new features, compatibility changes, and bug fixes, see the R2022a Release Notes in the Users Guide.
Among the missions supported by this release is the Fermi low Earth NASA mission, which uses the GPS point solution data type for ground based orbit determination using GMAT's new operational Extended Kalman Filter Smoother (EKFS) for operations.
Introducing Astrodynamics Workbench™
Thinking Systems has been developing an internal project, Astrodynamics Workbench™, while providing support of cusomers over the last two years. This "Dog Food" project was initially driven by the need for a solid multiple window interface on Linux platforms supporting proven GMAT numerics. Over the last year, it has grown to include features that provide support for emerging propulsion technologies and optimal maneuver planning in support of trajectories ranging from low Earth missions to truly deep space trajectories.
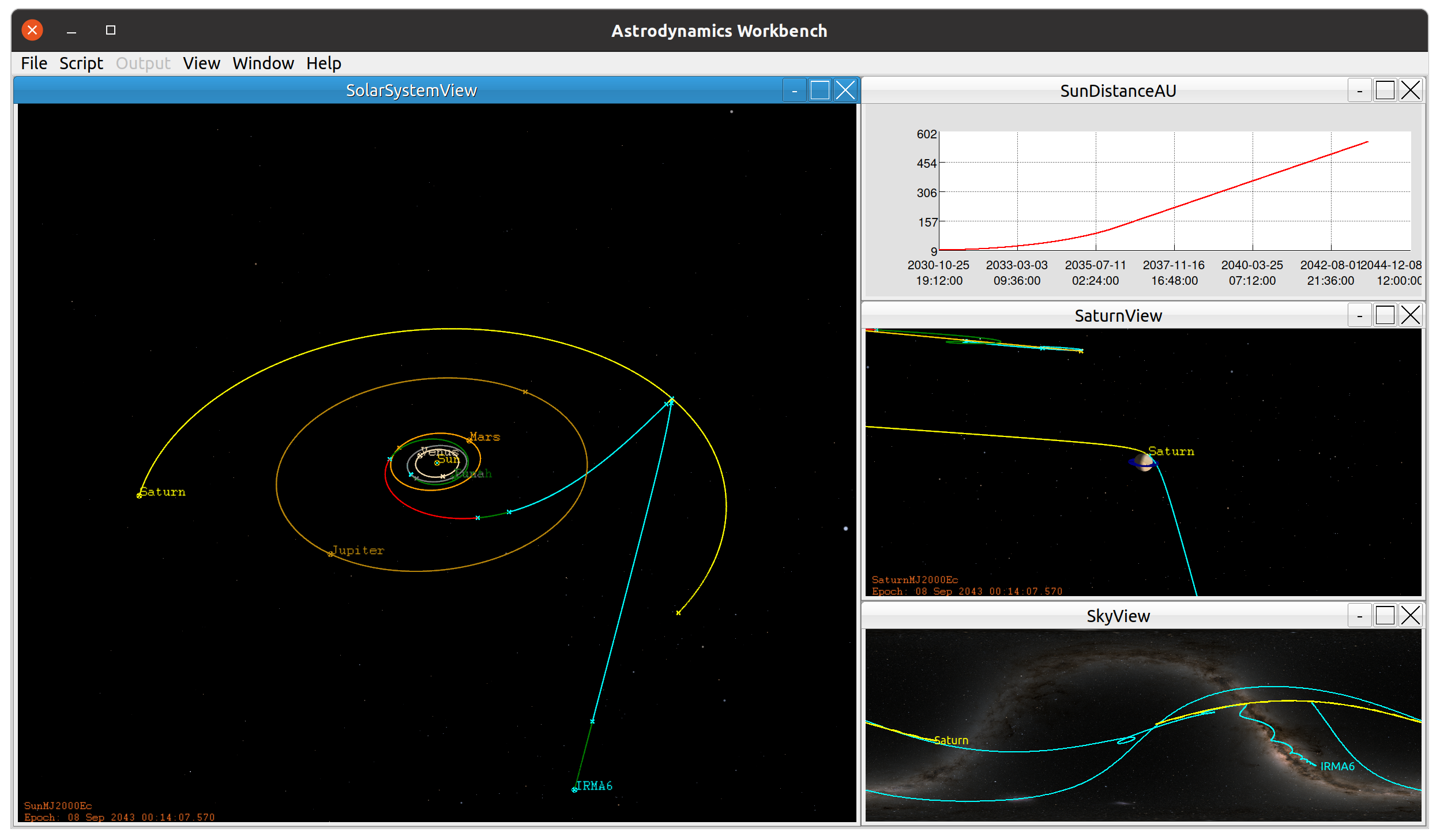
Availability Astrodynamics Workbench is a beta project, nearing readiness for release. Interested parties should contact the system architect, Darrel Conway with the subject line "Astrodynamics Workbench" for additional information.
Live demonstrations of Astrodynamics Workbench can also be seen at the 2021 AGU Fall Conference in New Orleans. Contact Dr. Conway to set one up.
Plugins and Enhancements for GMAT R2020a
Thinking Systems is pleased to announce general availability of the VF13ad optimizer and a beta quality TLE propagator for GMAT R2020a for Linux, Windows, and Mac OS X users. These libraries are free for all GMAT users. They can be downloaded on our downloads page. The figure below shows a collection of spacecraft, all propagated with the TLE propagator.
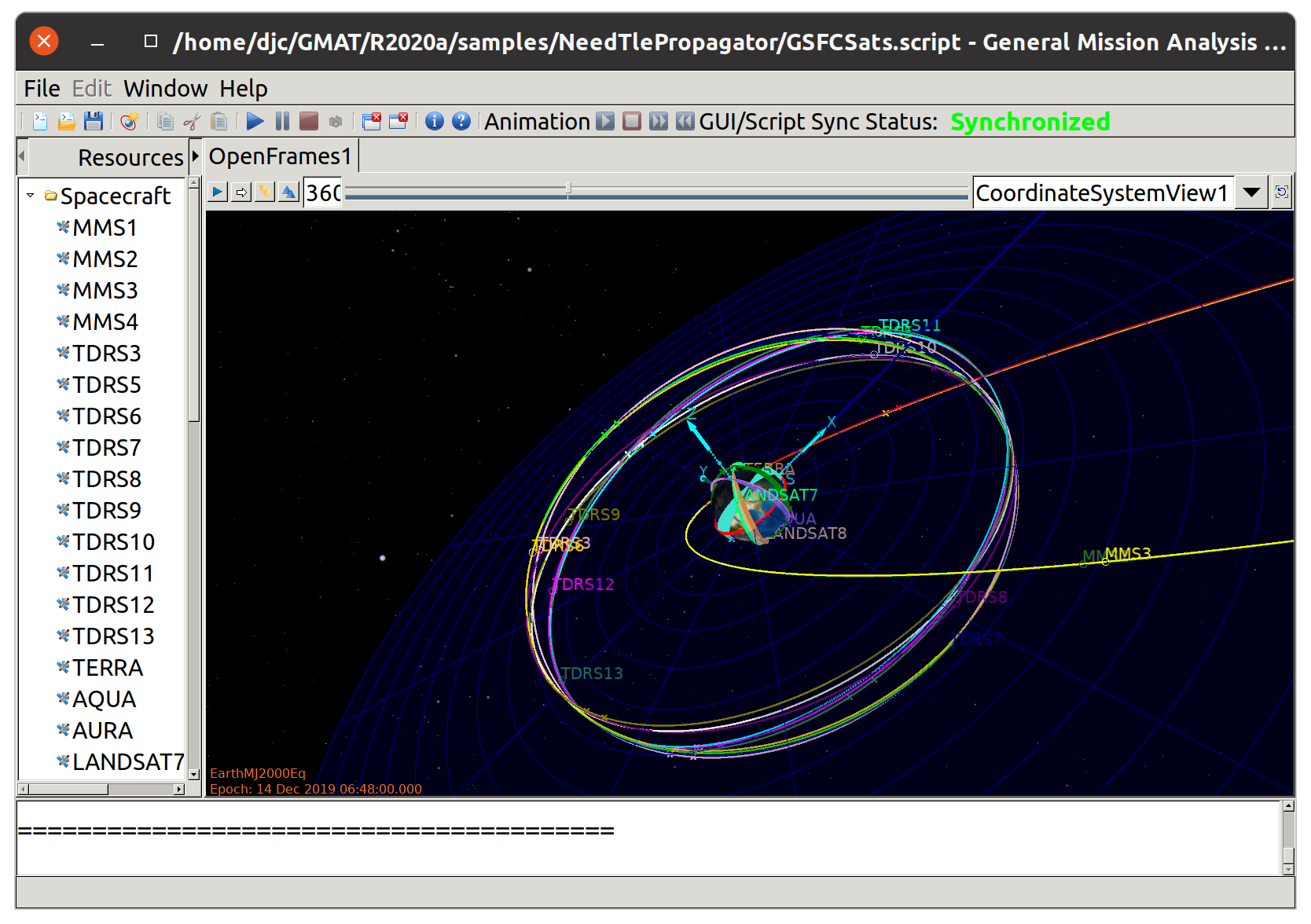
Additionally, we have repackaged the R2020a components that depend on Python for Ubuntu 20.04 users, making the Python interfaces for R2020a fully functional for users on that LTS release of Ubuntu Linux. Ubuntu 20.04 uses Python 3.8 as its default Python configuration. GMAT R2020a for Ubuntu was built using Python 3.6. The GMAT components in the bundled package on our downloads page enables the Python interface and the GMAT API for Ubuntu 20.04 users.
GMAT R2020a Released

GMAT R2020a has passed final testing and is now available for download from SourceForge. This release is a significant update to the system, incorporating many new features that enhance its usability in analysis and operations.
New features in this release include
- A new 3D graphics engine based on OpenFrames.
- The first production-quality C++ release of the Collocation Stand-Alone Library and Toolkit (CSALT), a new optimal control subsystem that supports finite-thrust optimization.
- A new (beta) API developed to provide users low-level access to GMAT functionality and to support interoperability between NASA's GMAT, Copernicus, and MONTE software applications, a new continuous thrust mission design and navigation feature. More information about the GMAT API can be found in
- A new (alpha) Extended Kalman Filter Smoother with process noise.
The new release supports operations for the following NASA missions:
- The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) began using GMAT for operational OD in June 2018, replacing GTDS.
- In April 2018, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) mission launched. TESS used GMAT as its primary tool for mission design and maneuver planning from proposal development through operations.
- The GMAT team is currently integrating CSALT into GSFC's Core Flight System (cFS) to demonstrate the ability to perform optimal control onboard.
Additional new features can be found on the GMAT R2020a release notes. Thinking Systems is proud to have participated in development of these features.
Ubuntu 20.04 Users GMAT R2020a's Python interface and the Python API were built using Ubuntu 18.04 LTS and Python 3.6. Ubuntu 20.04 is packaged with Python 3.8, requiring an update to the GMAT libraries. A build of these components for Ubuntu users, made with Python 3.8, can be found on the Thinking Systems Downloads page.
Announcing VF13ad and TLE Propagation Packages for GMAT R2020a
The VF13ad Plugin
Thinking Systems has received a distribution license from the Computational Mathematics Group at the Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC) Rutherford Appleton Laboratory to distribute compiled copies the VF13ad optimizer for use with GMAT. The VF13ad optimizer is a SQP-based Nonlinear Programming solver available in the HSL. HSL is a collection of Fortran codes for large-scale computation, available at http://www.hsl.rl.ac.uk/.
Users of previous releases of GMAT were required to build the VF13 optimizer from source code, using shell code available at SourceForge. This license allows free distribution by Thinking Systems of the VF13ad plugin component. The VF13 packages are coming shortly after GMAT R2020a is made publicly available for download.
A TLE Propagator
Thinking Systems is developing a propagation component designed so that GMAT users can propagate two-line element sets directly from online sources like Celestrak. This component will be available for download shortly after the public release of GMAT R2020a. Code for the component is available on GitLab.
The R2020a TLE propagator build is a beta-release while final updates are made to resolve small coordinate system issues and to test the stability of the plugin.
GMAT R2018a Released

GMAT R2018a has passed final testing and is now available for download from SourceForge. This release is a significant update to the system, incorporating many new features that enhance its usability in analysis and operations.
The new release supports operations for the following NASA missions:
- The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) mission: Maneuver planning and product generation.
- The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) mission: Orbit determination.
- The Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) mission: Maneuver planning, orbit determination, and product generation.
- The WIND mission: Maneuver planning, orbit determination, and product generation.
- The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) mission: Mission design and maneuver planning.
- The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) mission: Orbit determination.
The new features incorporated into GMAT R2018a include:
- GMAT now contains a built-in optimizer called Yukon, developed by the GMAT team. The optimizer uses an SQP line search algorithm with an active set QP-subproblem algorithm. Yukon is designed for small scale problems, in settings that could be optimized using the VF13ad optimizer in earlier GMAT releases. Yukon is not appropriate for large, sparse optimization problems.
- GMAT's Estimation System has been enhanced with these major features:
- Extended precision time has been implemented surgically to improve estimation.
- A "freeze" feature that stops data editing after a specified number of batch iterations.
- GMAT now implements and allows selection of the Marini troposperic model.
- GMAT now extends the plug-in interfaces to include GUI plug-in components.
Additional new features can be found on the GMAT R2018a release notes. Thinking Systems is proud to have participated in development of all of these features.